or start from open source methods. Learn more about OneLab softwareUse OneLab
Single-Step SYBR® Green RT-qPCR
This example method provides a freely adjustable framework for measuring the adaptability of the OneLab environment to workflows from different application fields. It helps to understand various nuances of the code-free, universal protocol designer and provides general indications as to the feasibility of a project. Scripts generally require fine adjustment to correct for variables and support specific labware implementation.
Overview
Quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) is highly suited for the analysis of gene expression allowing for rapid and sensitive detection of RNA targets even at low abundance. It typically comprises two reactions, following RNA extraction from cells and tissue samples. Complementary DNA is synthesized by reverse transcription of target RNA. Then, the resulting cDNA is amplified by PCR using a DNA polymerase and specific primers.
Conventional PCR Challenges
PCR comes with its share of challenges that have varying impacts on the efficiency of the reaction. The most common issues are related to improper pipetting and DNA contamination during sample preparation. There can be various sources of contamination during PCR. A common observation is excessive or unexpected signal, typically caused by contamination of reagents with DNA material from previous reactions. Either of these sources of error results, at best in a costly failure of the experiment, and at worst, misleading data.
One-Step RT-qPCR Assay
The protocol described here involves a single-step RT-qPCR assay, in which reverse transcription and PCR amplification occur in the same tube using an optimized buffer (Figure 1). It uses the SYBR Green fluorogenic probe to monitor the accumulation of PCR products in real-time and subsequently quantify gene expression levels. The single-tube operation not only saves time and minimizes contamination risk, but also increases throughput by enabling a more automation-friendly procedure. It is ideal for applications where cDNA is not required for subsequent experiments.
The workflow comprises three phases:
1. Normalization of RNA samples
2. Preparation of a reagent mixture
3. Setting up PCR reactions
The single reagent mixture facilitates accurate dispensing of reagents and minimizes the loss of costly components, such as enzymes and primers. OneLab assists you during the preparation of the reagent mixture and PCR reactions by ensuring correct and accurate pipetting, which consequently helps to minimize sample-to-sample variation.
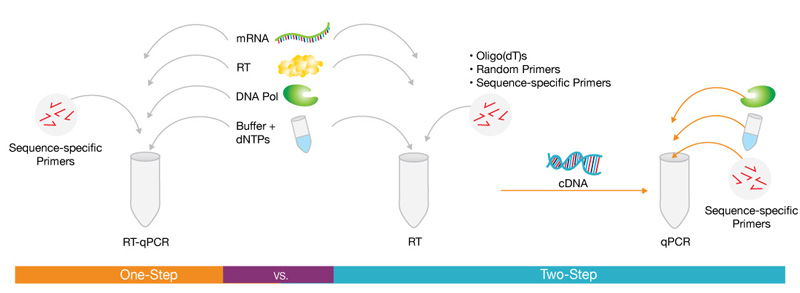
Figure 1: Schematic illustration highlighting the difference between one-step and two-step RT-qPCR.
In the one-step assay, reverse transcription and PCR reactions occur in a single tube and buffer, while in a two-step assay, the reverse transcription and PCR steps are performed separately.
Original image from spotlight article “Basic Principles of RT-qPCR”, in Molecular Biology Resource Library, Thermo Fisher.
Explore Brilliant II Master Mix Reagents for RT-qPCR from Agilent Technologies
Protocols

Contact info

 This is an open access protocol distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open access protocol distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. 