or start from open source methods. Learn more about OneLab softwareUse OneLab
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Gene Knockout
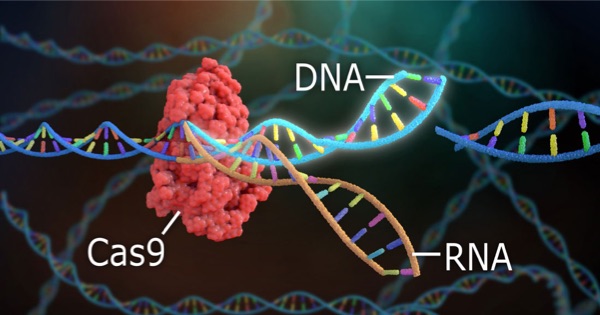
This example method provides a freely adjustable framework for measuring the adaptability of the OneLab environment to workflows from different application fields. It helps to understand various nuances of the code-free, universal protocol designer and provides general indications as to the feasibility of a project. Scripts generally require fine adjustment to correct for variables and support specific labware implementation.
Overview
CRISPR technology has become a commonly used tool for site-directed genome editing in various biological systems. It is an easy, versatile, and robust technique for conducting gene knockout and studying gene function. The isolation of successfully edited single-cell colonies depends not only on the quality of cell preparation and the efficiency of transfection but also on the accurate execution and annotation of critical liquid handling steps such as serial dilutions.
After the transfection of vectors coding for the guide RNA and Cas9 protein, CRISPR-Cas9 is used to create a targeted, sequence-specific double-strand DNA break in the gene of interest (Figure 1). The broken sites are repaired by the endogenous non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) machinery, often leading to the formation of small insertions or deletions (INDELs), which consequently result in gene knockout. Candidate clones grown from single cells are isolated and screened to identify those containing the mutation. Finally, DNA sequencing of the mutant allele(s) is performed for positive clones.
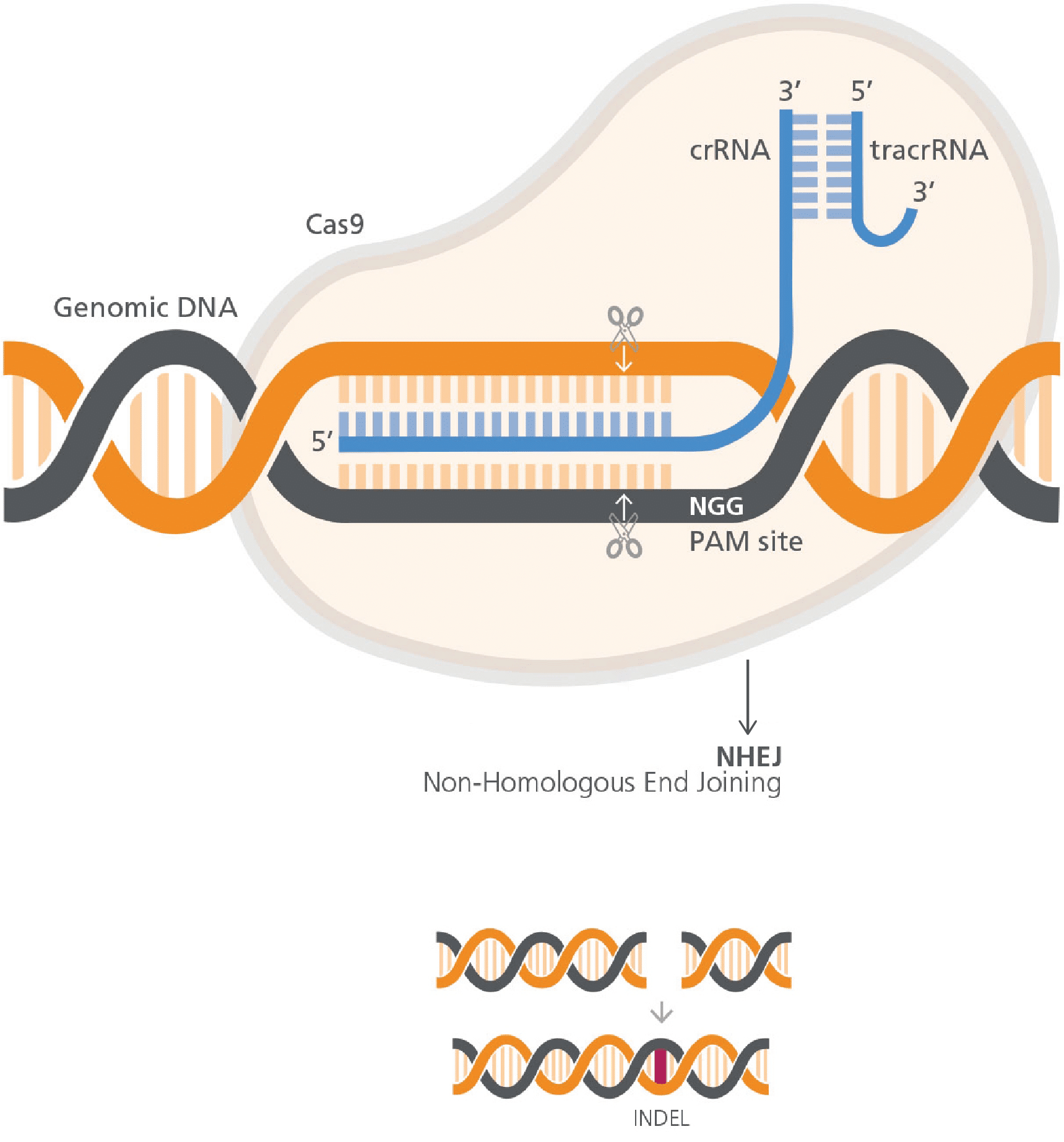
Figure 1: Site-specific double-strand break of the target DNA sequence mediated by the CRISPR-Cas9 machinery. The schematic is adapted from the technical bulletin "Genome Editing with Direct Cas9 RNP Delivery Design Considerations" by STEMCELL Technologies Inc. (1).
Watch the video tutorial about the gene knockout experiment using CRISPR-Cas9 technology
(1) Technical Bulletin | Genome Editing with Direct Cas9 RNP Delivery Design Considerations. STEMCELL Technologies Inc. (Document # 27083, version 1.0.1, Jun 2018)
Download the original protocol "Gene knockout without donor"
Protocols
Contact info

 This is an open access protocol distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open access protocol distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. 